Understanding Your Cycle: How to Track and Optimize Your Menstrual Health
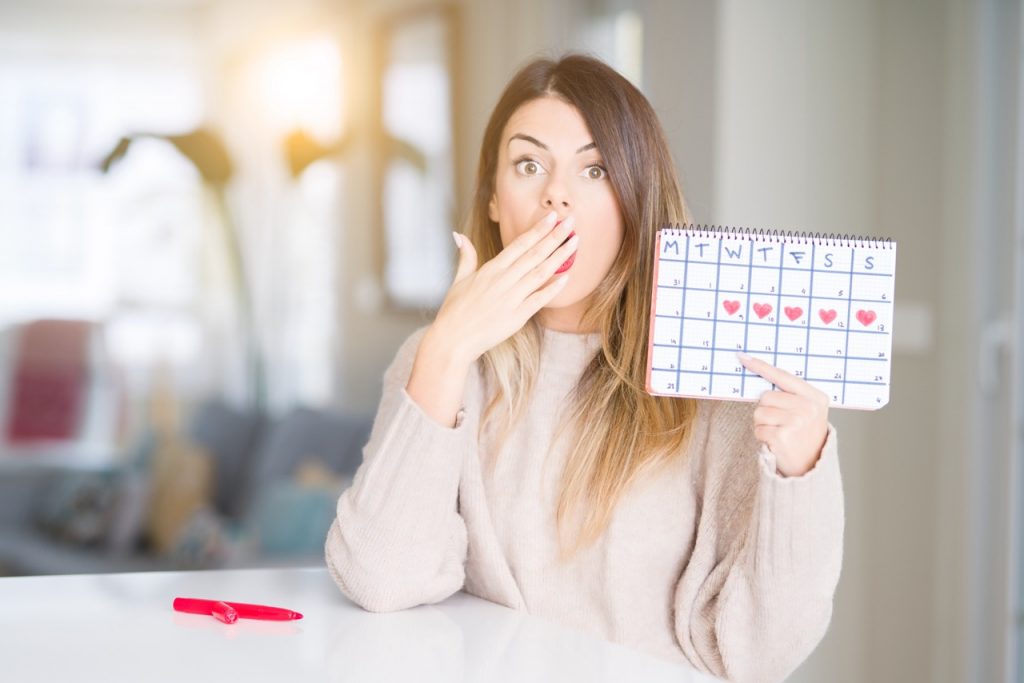

Your menstrual cycle is more than just a monthly occurrence—it’s a vital sign of your overall health. Understanding your cycle can help you track ovulation, manage symptoms, and identify potential health concerns. A typical menstrual cycle lasts 21 to 35 days, but every woman’s cycle is unique. By learning to track your cycle, you can gain valuable insights into your reproductive health.
How to Track Your Cycle
Start by recording the first day of your period each month, which marks Day 1 of your cycle. Apps, calendars, or journals can help you keep track of your cycle length and symptoms like cramps, mood changes, and energy levels. Ovulation typically occurs around the midpoint of your cycle, which is the optimal time for conception. Tracking signs like cervical mucus changes, basal body temperature, and ovulation test results can help pinpoint ovulation.
Why It’s Important
Tracking your cycle can reveal irregularities, such as skipped periods, unusually heavy bleeding, or cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days. These can be signs of conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, or hormonal imbalances. If you notice irregularities, consult your OB-GYN for evaluation.
Optimizing Your Cycle
A healthy lifestyle can support a regular cycle. Focus on balanced nutrition, stress management, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Supplements like magnesium and omega-3 fatty acids may also help with PMS symptoms. If you’re experiencing severe pain, heavy bleeding, or other disruptive symptoms, speak with your healthcare provider to explore treatment options.